Actualité volcanique, Articles de fond sur étude de volcan, tectonique, récits et photos de voyage
Par Bernard Duyck
The mid-Arctic rift has long been considered geologically inactive ... is it because of its retracted position, its significant ice cover, or its small spacing ratio (0.05 cm / year) and low seismicity .
The Gakkel Ridge rift was hit by an earthquake of M 4.5 March 6, 2014; although with moderate magnitude, this earthquake is associated with a large release of methane into the atmosphere suggesting that the fault movement is not limited to the epicenter but affect the entire fault system of the Gakkel Ridge, where hydrothermal vents are documented, but little is known about the number and distribution.
This information shows that this vent system is a source of heat and fluids powerful, which can influence the climate of the Arctic and the melting of the ice cap.
The Mid-Arctic rift and its various basins and ridges
Research on the Gakkel Ridge began in 1999 when a nuclear submarine has detected the presence of active volcanoes along the rift.
In 2001, the icebreakers allowed to harvest rock samples and observing many hydrothermal vents.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (WHOI) expedition in 2007 discovered unconsolidated pyroclastic deposits, indicating that a recent and strong submarine eruption marked a significant portion of the Gakkel Ridge. Chemical analysis of deposits indicates an instability of the volcanic beds more than ten times higher than the results achieved on the deep oceanic rift systems. Microbiological analysis also shows chemosynthetic life known to be associated with hydrothermal vents.
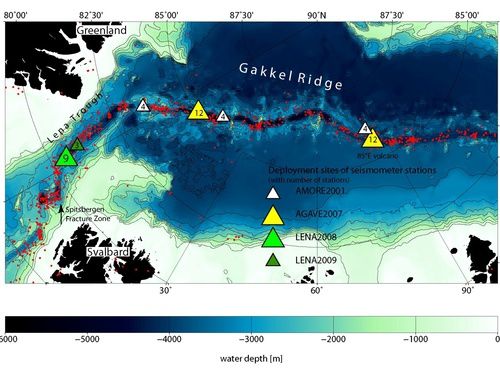
Earthquakes along the Mid-Arctic Ridge system (red dots) and installation sites of seismometers (triangles) - doc Awi.de
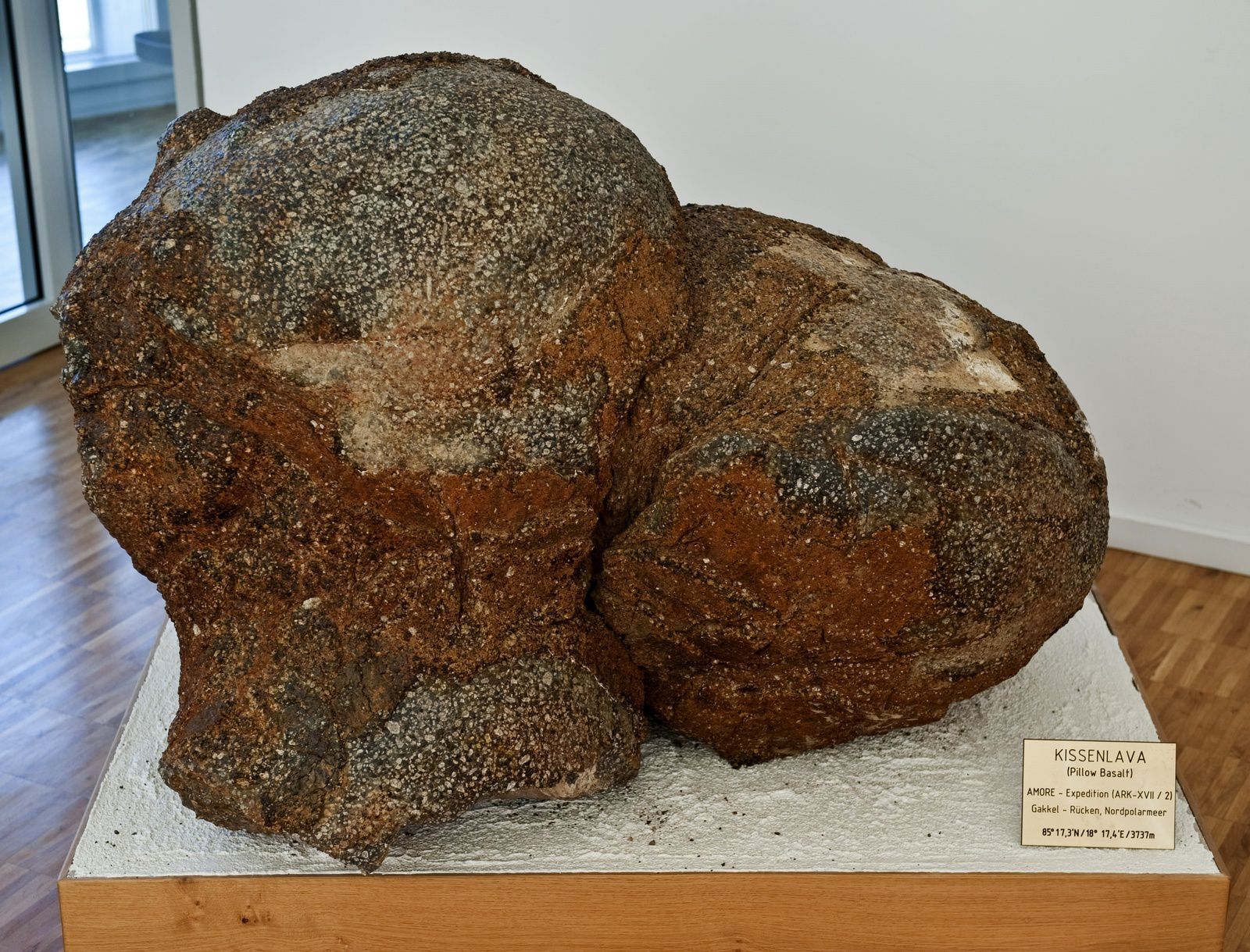
Pyroclatic deposits photographed and collected during the WHOI expedition July 2007 on the Gakkel Ridge - a. pyroclastic materials overcame a pillow lavas structure - b. Talus of blocks presumably representing the ejecta of a vulcanian explosion of the volcano Oden - c. pyroclastic materials, glassy, and granular - d. fragment of the wall of a bubble from the pyroclastic deposit - Doc. Sohn et al. / WHOI / GVP
On the left, cross section of the dorsal Gakkel - right, another cut of the ridge and its surroundings (exaggerated) - a click to enlarge - Doc. Hannes Grobe, Alfred Wegener Institute - own work, data from POLARSTERN Expedition ARK-VIII3 in 1991.
... This means that the spreading ratios and seismic activity are not necessarily correlated with the intensity and distribution of the heat flow, and these findings is to apply to all the deep ocean rifts.
Too few climatologists considered the heat induced at the Medio-Arctic rift as a possible explanation of the glacial melting in the Arctic, and its connection with the subglacial planktonic proliferation recently discovered.
Sources :
- Climate change dispatch - Update on Geothermal Heat and Arctic Ocean Sea Ice Melt - link
- Global Volcanism Program – East Gakkel ridge at 85 E – link
- WHOI – Dive discover expedition 11 - link
Thème Magazine - Hébergé par Overblog





/image%2F0935525%2F20150109%2Fob_818185_gakkel-ridge-cross-section.jpg)
/image%2F0935525%2F20150109%2Fob_af7c0e_hannes-grobe-alfred-wegener-institute.png)

