Actualité volcanique, Articles de fond sur étude de volcan, tectonique, récits et photos de voyage
Par Bernard Duyck
A recent image of the Yellowstone magma chamber has been published by the Volcano Observatory, following measures of seismic tomography carried out by seismologists from the University of Utah and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology.
The resulting model reveals a large area where P-waves travel more slowly, and interpreted as resulting from the presence of partially molten hot rocks ... the magma chamber is 90 km. length is between 5 and 17 km. deep, and is 2.5 times greater that thinking in the previous study.
This "growth" is due to an extension of the coverage by the seismograph network in the NE of the Park.
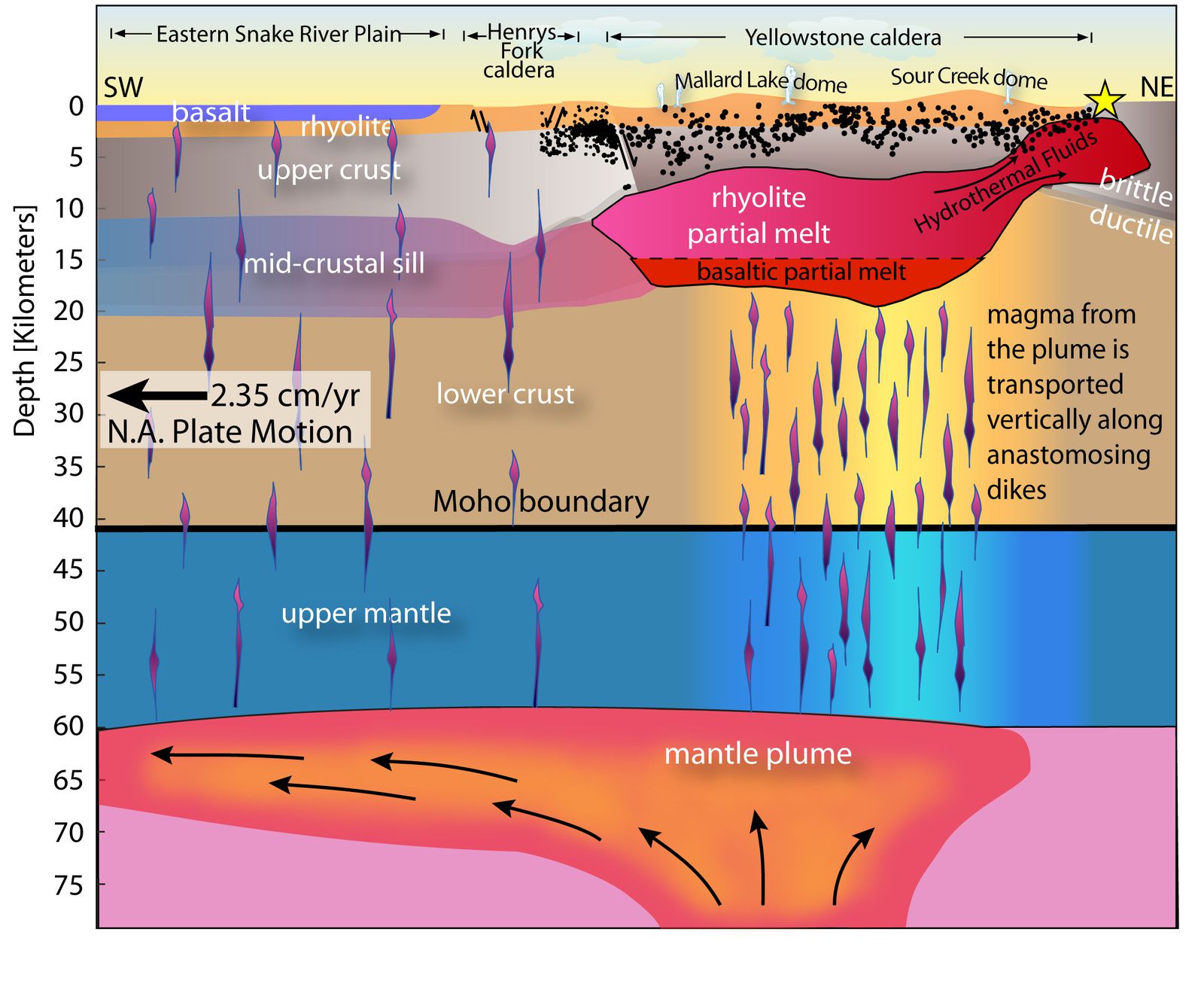
Schematic cross under the Yellowstone / Snake river plain, oriented SW-NE, describing the Yellowstone magma chamber, the rise of magma from the mantle, the move of the tectonic plate above the mantle plume - doc.Farrell et al. / YVO / journal Geophysical Research Letters
The low velocity zone extends up to 15 km. northeast of the Yellowstone caldera at a depth of less than 5 km. It is to be linked with the presence of high temperature fluids (gases, hot water, and other fluids) as indicated by the gravity measurements.
The magma chamber contains 5 to 15% of molten rock, occupying the spaces between the solid / crystalline materials ... we are far from the 50% of molten rock necessary for an eruption.
Progress towards the NE of the magmatic system corresponds to the movement of the North American plate to the west, above the stationary mantle plume (Yellowstone hot spot), located at a depth of 60-90 km.
The Yellowstone Volcano Observatory says, if need be, that these details on the size of the magma chamber in no way reflect an increase of volcanic risk.
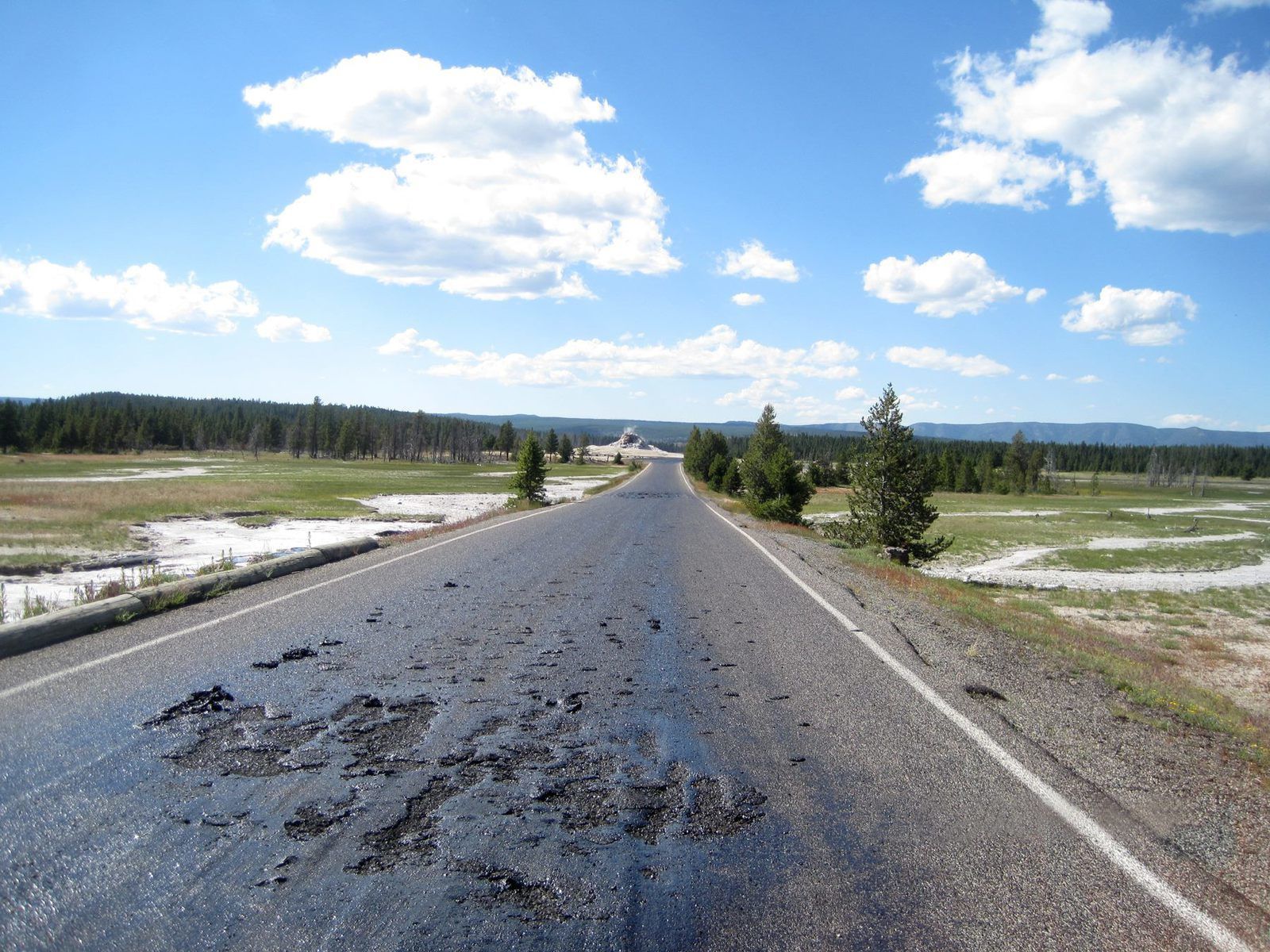
Firehole Lake Drive closed due to high temperature of the basement - Photo Yellowstone National Park
Similarly, closing on July 10 of Firehole Lake Drive, a one-way road that passes through Great Fountain Geyser, White Dome Geyser and Firehole lake, by road safety measures and maintenance after melting the asphalt overlay, should not announce any disaster.
Changes in temperature of the hydrothermal system regularly damage the road surface and the boardwalk, although this event is disruptive in the tourist season.
Thème Magazine - Hébergé par Overblog